本文内容来源于网络收集
作者:冰河
来源:冰河技术公众号
- 本章难度:★★☆☆☆
- 本章重点:用最简短的篇幅介绍迭代器模式最核心的知识,理解迭代器模式的设计精髓,并能够灵活运用到实际项目中,编写可维护的代码。
一、概述
给定一个语言,定义它的文法的一种表示,并定义一个解释器,这个解释器使用该表示来解释语言中的句子。
二、适用性
1.访问一个聚合对象的内容而无需暴露它的内部表示。
2.支持对聚合对象的多种遍历。
3.为遍历不同的聚合结构提供一个统一的接口(即:支持多态迭代)。
三、参与者
1.Iterator 迭代器定义访问和遍历元素的接口。
2.ConcreteIterator 具体迭代器实现迭代器接口。 对该聚合遍历时跟踪当前位置。
3.Aggregate 聚合定义创建相应迭代器对象的接口。
4.ConcreteAggregate 具体聚合实现创建相应迭代器的接口,该操作返回ConcreteIterator的一个适当的实例。
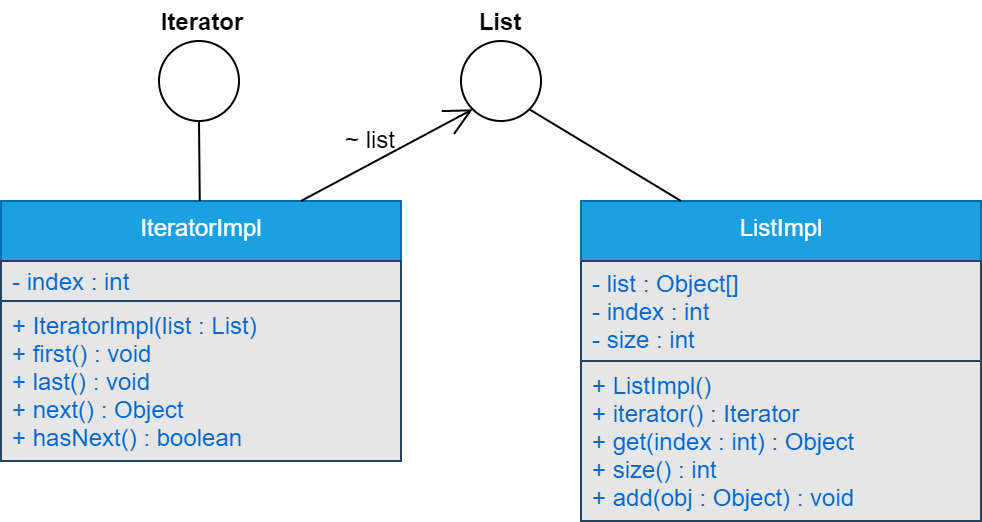
四、类图
五、示例
Iterator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description Iterator
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public interface Iterator {
Object next();
void first();
void last();
boolean hasNext();
}
|
ConcreteIterator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description ConcreteIterator
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class IteratorImpl implements Iterator {
private List list;
private int index;
public IteratorImpl(List list) {
index = 0;
this.list = list;
}
@Override
public void first() {
index = 0;
}
@Override
public void last() {
index = list.size();
}
@Override
public Object next() {
Object obj = list.get(index);
index++;
return obj;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return index < list.size();
}
}
|
Aggregate
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description Aggregate
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public interface List {
Iterator iterator();
Object get(int index);
int size();
void add(Object obj);
}
|
ConcreteAggregate
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description ConcreteAggregate
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class ListImpl implements List{
private Object[] list;
private int index;
private int size;
public ListImpl() {
index = 0;
size = 0;
list = new Object[100];
}
@Override
public Iterator iterator() {
return new IteratorImpl(this);
}
@Override
public Object get(int index) {
return list[index];
}
@Override
public int size() {
return this.size;
}
@Override
public void add(Object obj) {
list[index++] = obj;
size++;
}
}
|
Test
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description 测试类
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ListImpl();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
//第一种迭代方式
Iterator it = list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
System.out.println("=====");
//第二种迭代方式
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
}
}
|
Result
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
a
b
c
=====
a
b
c
|