本文内容来源于网络收集
作者:冰河
来源:冰河技术公众号
- 本章难度:★★☆☆☆
- 本章重点:用最简短的篇幅介绍命令模式最核心的知识,理解命令模式的设计精髓,并能够灵活运用到实际项目中,编写可维护的代码。
一、概述
将一个请求封装为一个对象,从而可以用不同的请求对客户端进行参数化;对请求排队或记录请求日志,以及支持可撤消的操作。
二、适用性
1.抽象出待执行的动作以参数化某个对象。
2.在不同的时刻指定排列和执行请求。
3.支持取消操作。
4.支持修改日志,这样当系统崩溃时,这些修改可以被重做一遍。
5.用构建在原语操作上的高层抽象操作构造一个系统。
三、参与者
1.Command 声明执行操作的接口。
2.ConcreteCommand 将一个接收者对象绑定于一个动作。 调用接收者相应的操作,以实现Execute。
3.Client 创建一个具体命令对象并设定它的接收者。
4.Invoker 指定该命令执行某个请求。
5.Receiver 指定如何实施与执行一个请求相关的操作。任何类都可能作为一个接收者。
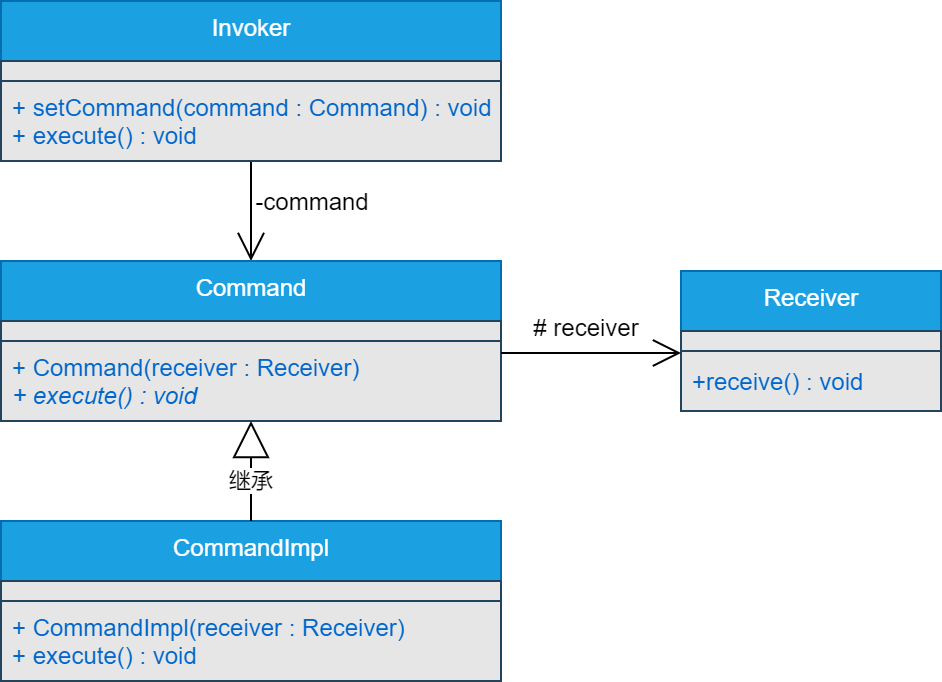
四、类图
五、示例
Command
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description Command
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public abstract class Command {
protected Receiver receiver;
public Command(Receiver receiver) {
this.receiver = receiver;
}
public abstract void execute();
}
|
ConcreteCommand
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description ConcreteCommand
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class CommandImpl extends Command{
public CommandImpl(Receiver receiver) {
super(receiver);
}
@Override
public void execute() {
receiver.receive();
}
}
|
Invoker
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description Invoker
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class Invoker {
private Command command;
public void setCommand(Command command) {
this.command = command;
}
public void execute() {
command.execute();
}
}
|
Receiver
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description Receiver
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class Receiver {
public void receive() {
System.out.println("This is Receive class!");
}
}
|
Test
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description 测试类
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Receiver rec = new Receiver();
Command cmd = new CommandImpl(rec);
Invoker i = new Invoker();
i.setCommand(cmd);
i.execute();
}
}
|
Result