本文内容来源于网络收集
作者:冰河
来源:冰河技术公众号
- 本章难度:★★☆☆☆
- 本章重点:用最简短的篇幅介绍桥接模式最核心的知识,理解桥接模式的设计精髓,并能够灵活运用到实际项目中,编写可维护的代码。
一、概述
将抽象部分与它的实现部分分离,使它们都可以独立地变化。
二、适用性
1.不需要在抽象和它的实现部分之间有一个固定的绑定关系,在程序运行时刻实现部分程序可以被选择或者切换。
2.类的抽象以及它的实现都应该可以通过生成子类的方法加以扩充。 这时Bridge模式可以对不同的抽象接口和实现部分进行组合,并分别对它们进行扩充。
3.对一个抽象的实现部分的修改应对其他业务不产生影响,即其他业务的代码不必重新编译。
4.需要在多个对象间共享实现(可能使用引用计数),但同时需要对其他业务无感知。
三、参与者
1.Abstraction
定义抽象类的接口。 维护一个指向Implementor类型对象的引用(指针)。
2.RefinedAbstraction
扩充由Abstraction定义的接口。
3.Implementor
定义实现类的接口,该接口不一定要与Abstraction的接口完全一致。 事实上这两个接口可以完全不同。 一般来讲,Implementor接口仅提供基本操作,而Abstraction则定义了基于这些基本操作的较高层次的操作。
4.ConcreteImplementor
实现Implementor接口并定义它的具体实现。
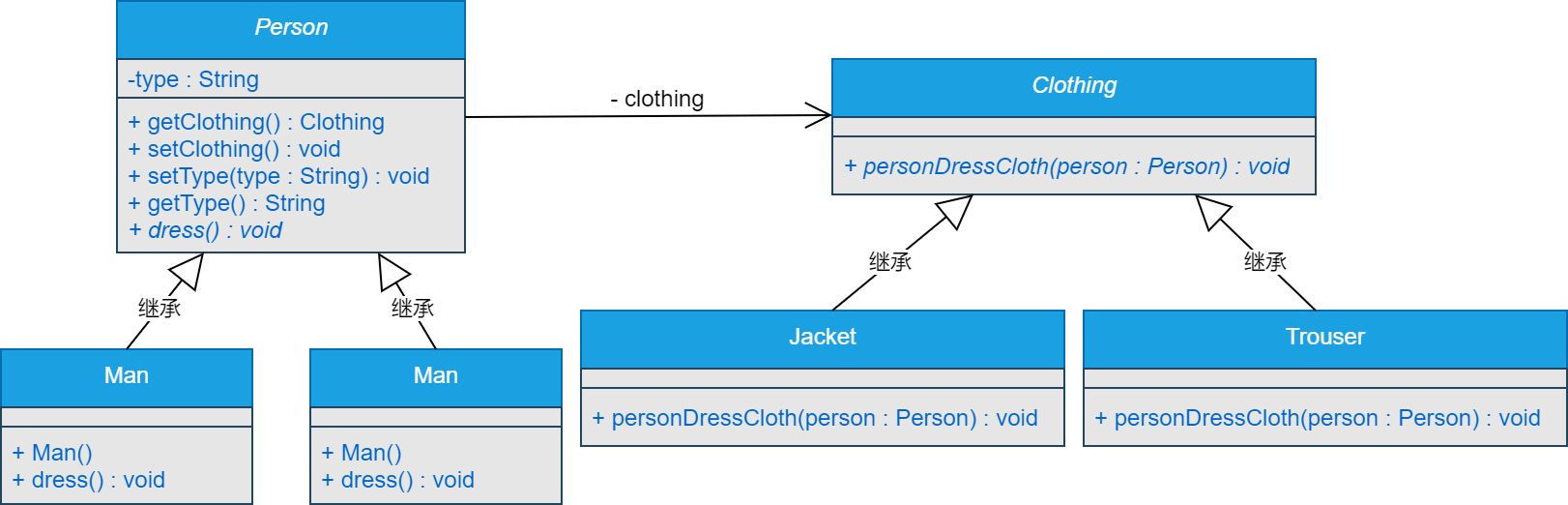
四、类图
五、示例
Abstraction
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description 定义Abstraction Person类
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public abstract class Person {
private Clothing clothing;
private String type;
public Clothing getClothing() {
return clothing;
}
public void setClothing(Clothing clothing) {
this.clothing = clothing;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getType() {
return this.type;
}
public abstract void dress();
}
|
RefinedAbstraction
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description 定义RefinedAbstraction类Man
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class Man extends Person{
public Man() {
setType("男人");
}
@Override
public void dress() {
Clothing clothing = getClothing();
clothing.personDressCloth(this);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description 定义RefinedAbstraction类Lady
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class Lady extends Person {
public Lady() {
setType("女人");
}
@Override
public void dress() {
Clothing clothing = getClothing();
clothing.personDressCloth(this);
}
}
|
Implementor
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description 定义Implementor 类Clothing
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public abstract class Clothing {
public abstract void personDressCloth(Person person);
}
|
ConcreteImplementor
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description 定义ConcreteImplementor类Jacket
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class Jacket extends Clothing{
@Override
public void personDressCloth(Person person) {
System.out.println(person.getType() + "穿马甲");
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description 定义ConcreteImplementor类 Trouser
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class Trouser extends Clothing {
@Override
public void personDressCloth(Person person) {
System.out.println(person.getType() + "穿裤子");
}
}
|
Test
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description 测试类
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person man = new Man();
Person lady = new Lady();
Clothing jacket = new Jacket();
Clothing trouser = new Trouser();
jacket.personDressCloth(man);
trouser.personDressCloth(man);
jacket.personDressCloth(lady);
trouser.personDressCloth(lady);
}
}
|
Result
1
2
3
4
|
男人穿马甲
男人穿裤子
女人穿马甲
女人穿裤子
|