本文内容来源于网络收集
作者:冰河
来源:冰河技术公众号
- 本章难度:★★☆☆☆
- 本章重点:用最简短的篇幅介绍外观模式最核心的知识,理解外观模式的设计精髓,并能够灵活运用到实际项目中,编写可维护的代码。
一、概述
为子系统中的一组接口提供一个一致的界面,Facade模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更加容易使用。
二、适用性
1.当为一个复杂子系统提供一个简单接口时,子系统往往因为不断演化而变得越来越 复杂。大多数模式使用时都会产生更多更小的类。这使得子系统更具可重用性,也更容 易对子系统进行定制,但这也给那些不需要定制子系统的用户带来一些使用上的困难。 Facade可以提供一个简单的缺省视图,这一视图对大多数用户来说已经足够,而那些需 要更多的可定制性的用户可以越过facade层。
2.客户程序与抽象类的实现部分之间存在着很大的依赖性。引入facade将这个子系统与客 户以及其他的子系统分离,可以提高子系统的独立性和可移植性。
3.当需要构建一个层次结构的子系统时,使用facade模式定义子系统中每层的入口点。 如果子系统之间是相互依赖的,你可以让它们仅通过facade进行通讯,从而简化了它们 之间的依赖关系。
三、参与者
1.Facade 知道哪些子系统类负责处理请求。 将客户的请求代理给适当的子系统对象。
2.Subsystemclasses 实现子系统的功能。 处理由Facade对象指派的任务。 没有facade的任何相关信息;即没有指向facade的指针。
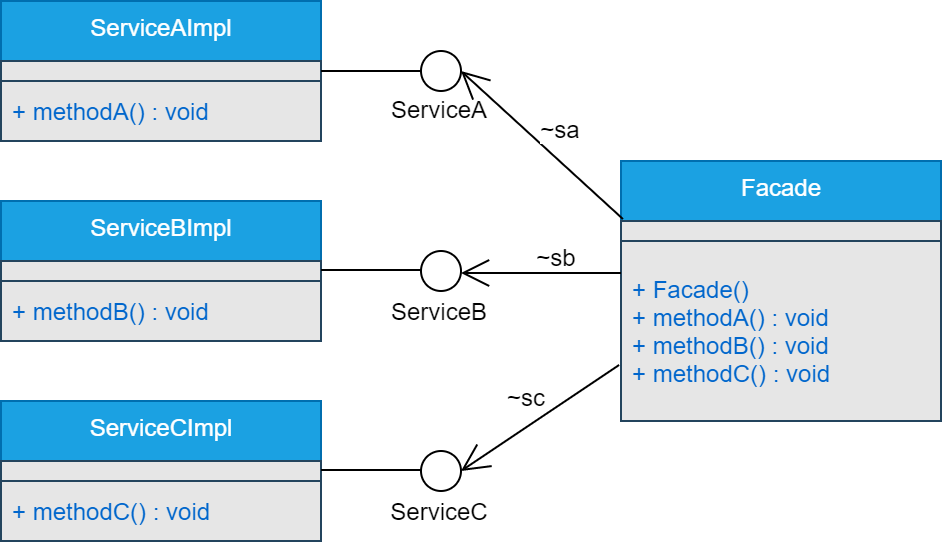
四、类图
五、示例
Facade
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description Facade
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class Facade {
ServiceA sa;
ServiceB sb;
ServiceC sc;
public Facade() {
sa = new ServiceAImpl();
sb = new ServiceBImpl();
sc = new ServiceCImpl();
}
public void methodA() {
sa.methodA();
sb.methodB();
}
public void methodB() {
sb.methodB();
sc.methodC();
}
public void methodC() {
sc.methodC();
sa.methodA();
}
}
|
Inerfaces
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description ServiceA
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public interface ServiceA {
void methodA();
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description ServiceB
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public interface ServiceB {
void methodB();
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description ServiceC
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public interface ServiceC {
void methodC();
}
|
Subsystemclasses
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description Subsystemclasses
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class ServiceAImpl implements ServiceA{
@Override
public void methodA() {
System.out.println("这是服务A");
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description Subsystemclasses
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class ServiceBImpl implements ServiceB{
@Override
public void methodB() {
System.out.println("这是服务B");
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description Subsystemclasses
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class ServiceCImpl implements ServiceC{
@Override
public void methodC() {
System.out.println("这是服务C");
}
}
|
Test
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
/**
* @author binghe(微信 : hacker_binghe)
* @version 1.0.0
* @description Test
* @github https://github.com/binghe001
* @copyright 公众号: 冰河技术
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServiceA sa = new ServiceAImpl();
ServiceB sb = new ServiceBImpl();
sa.methodA();
sb.methodB();
System.out.println("========");
//facade
Facade facade = new Facade();
facade.methodA();
facade.methodB();
}
}
|
Result
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
这是服务A
这是服务B
========
这是服务A
这是服务B
这是服务B
这是服务C
|